Introduction to Conditional Access
Conditional Access is a capability of Azure Active Directory that enables you to enforce controls on the access to apps in your environment based on specific conditions.
| When this happens | Then do this |
“When this happens” – is called conditional statement
An access attempt is made:
- To a cloud app*
- By users and groups*
Using:
- Condition 1 (for example, outside Corp network)
- Condition 2 (for example, device platforms)
“Then do this” – is called controls
Grant access with (AND):
- Requirement 1 (for example, MFA)
- Requirement 2 (for example, Device compliance
The combination of a conditional statement & controls represents a conditional access policy.
Why should I care about CA?
In a cloud-based architecture, a customer is going to need to move away from gateways. Conditional Access is the replacement of routing the cloud-service back on prem.
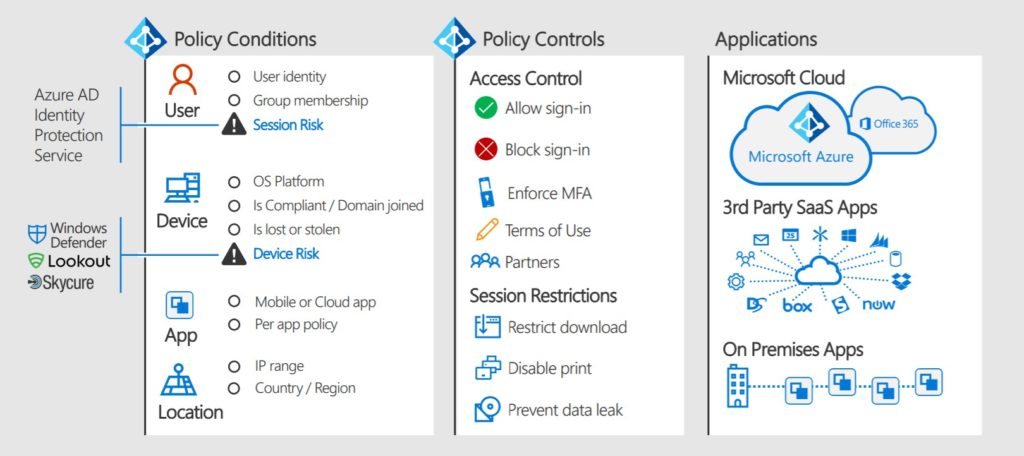
Understanding the following flow in-depth will allow you to understand how to build up policy and troubleshoot it later.
Conditions
These are conditions that you can include in a conditional access policy:
- Group Membership: Control a user’s access based on membership in a group.
- Location: Use the location of the user to trigger MFA or block when not on a trusted network.
- Device Platform: Use the device platform, such as iOS, Android, Windows Mobile, or Windows, as a condition for applying policy.
- Device-enabled: Device state, whether enabled or disabled, is validated during device policy evaluation. If you disable a lost or stolen device in the directory, it can no longer satisfy policy requirements.
- Sign-in and user risk: You can use Azure AD Identity Protection for conditional access risk policies. Conditional access risk policies help give your organization advance protection based on risk events and unusual sing-in activities.
Controls
These are controls that you can use to enforce a conditional access policy:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: You can require strong authentication through MFA. You can use Azure MFA or an on-premises MFA provider, combined with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS).
- Block: Block access when a user is not on a trusted network.
- Domain Joined/Compliant Devices: You can set a policy to only allow domain joined or Intune compliant devices.
- Session Based – Limit what the user can do in their session once granted access to the app (download/sync/print). Currently only supported for SharePoint Online and OneDrive.
Applications
You can set conditional access policies to protect these applications:
- SharePoint Online, to protect your organizations sites and documents
- Exchange Online, to protect your organizations email
- SaaS Applications that are connected to Azure AD for authentication
- On-premises Applications that are published by using Azure AD App Proxy
You can enforce a conditional access policy at the application level. Set access levels for applications and services inn the cloud or on-premises. The policy is applied directly to the website or service. The policy is enforced for access to the browser, and to applications that access the service.
Domain Joined vs. Compliant
Domain Joined Devices (Windows 7/8.1/10)
- Joined to On-Premises AD and have applied group policy for automated device registration against Azure AD
- A successfully registered device against Azure AD will receive a machine bound X.509 certificate used for device authentication
Compliant Devices
- Requires device to be enrolled into Intune (cannot be set by 3rd Party MDM)
- All MDM assigned compliance policies and settings are enforced for the device
- Example: PIN, Jainbroken, Encryption
Device Based
You can set device-based conditional access for these device types:
- Windows 10 Anniversary Update, Windows 8.1, and Windows 7
- Windows Server 2016, 2012 R2, 2012, and 2008 R2
- MacOS
- iOS devices (iPad, iPhone)
- Android Devices
Implications of iPadOS release:
- Apple has defined the default Safari user agent in iPadOS to match MacOS
- This means that browser connections appear as coming from MacOS
- This includes browser-based login in apps
- This means that CA Policies that target the MacOS platform will apply to iPadOS in Safari and non-MSAL/ADAL apps. This includes native mail app.
- For more information
Conditional Access Security Default
Security Defaults are included for all Azure AD tenants :
- Require MFA for admins
- End user protection
- Block legacy authentication
- Require MFA for Service Management